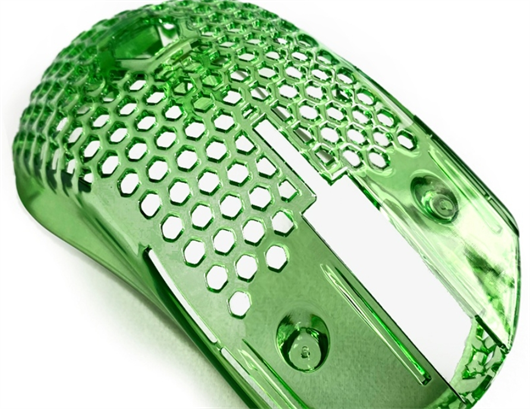
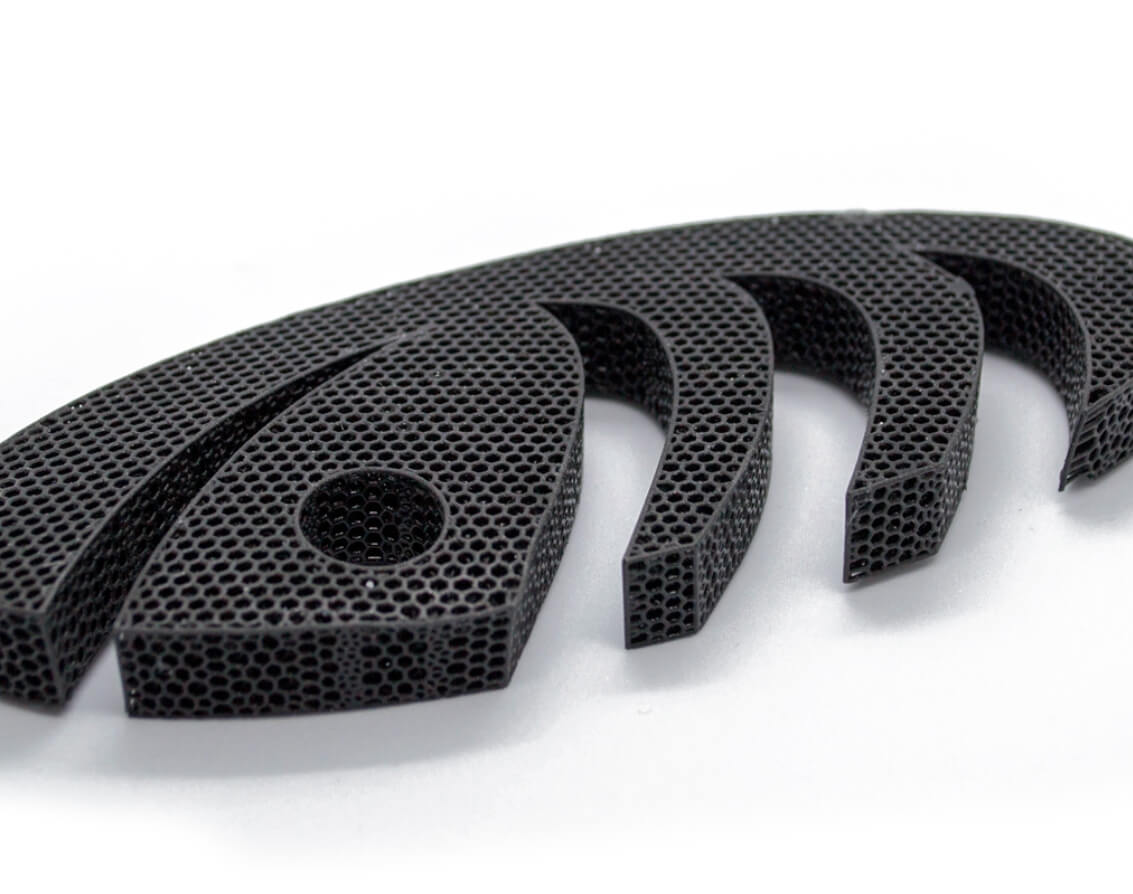
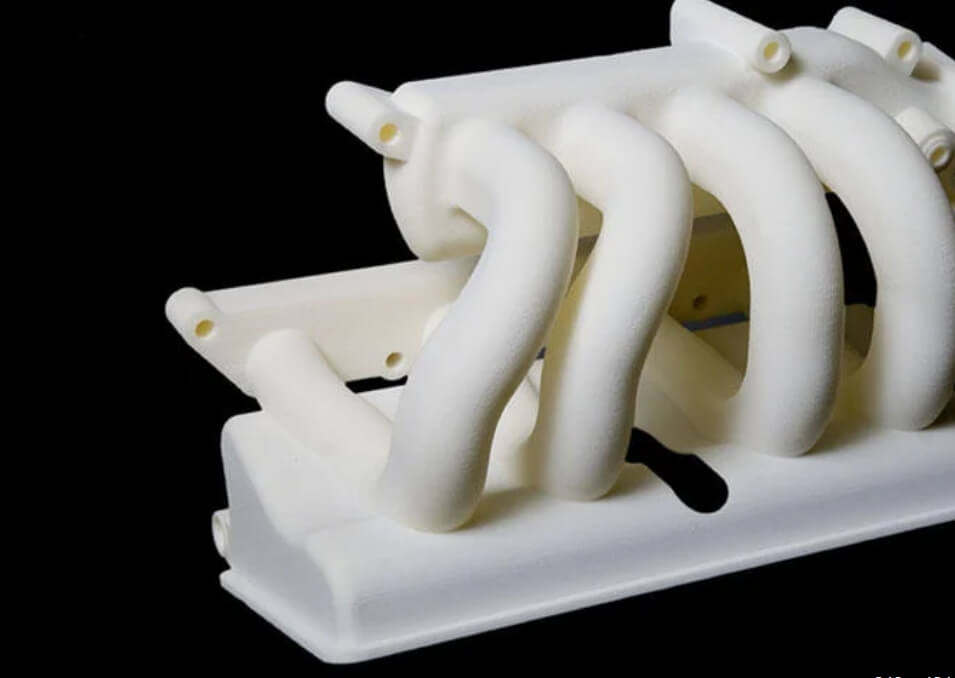
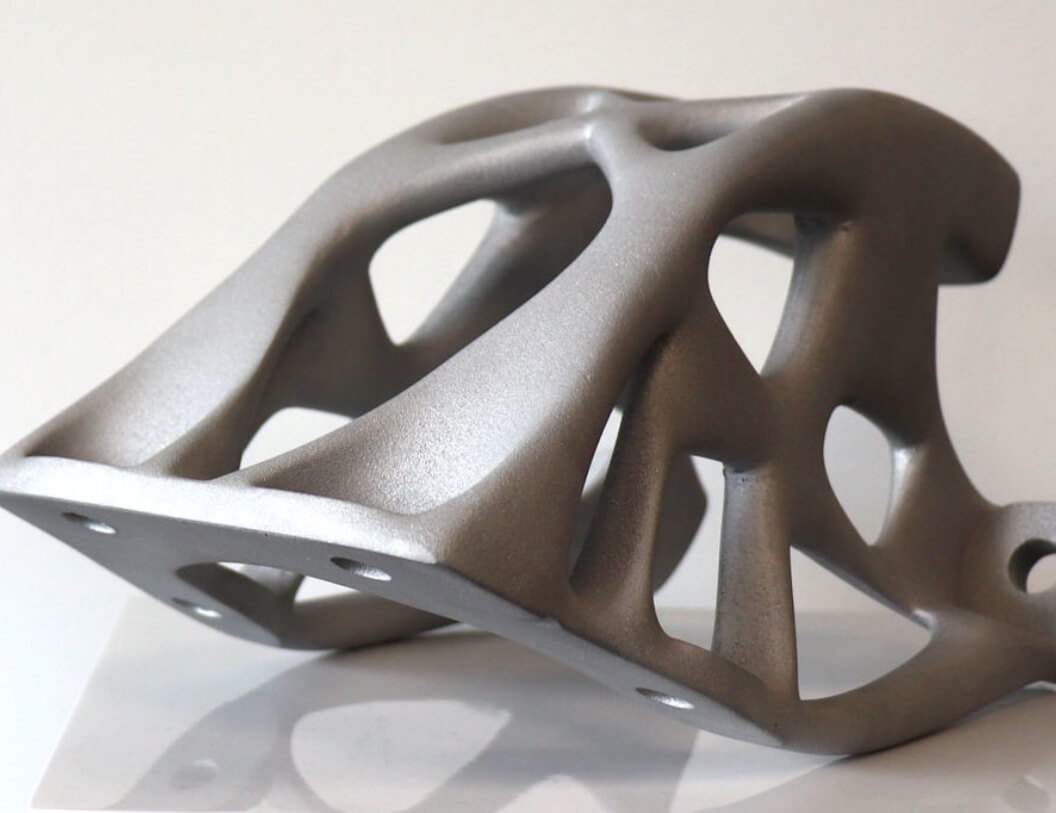
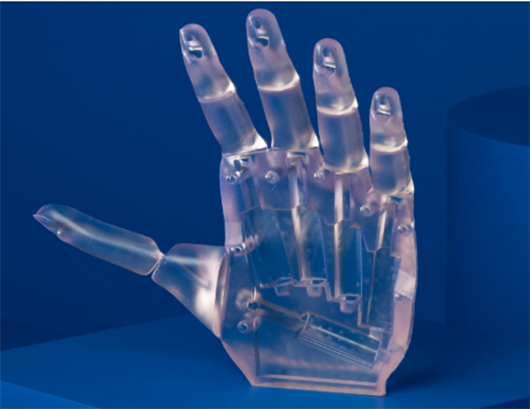
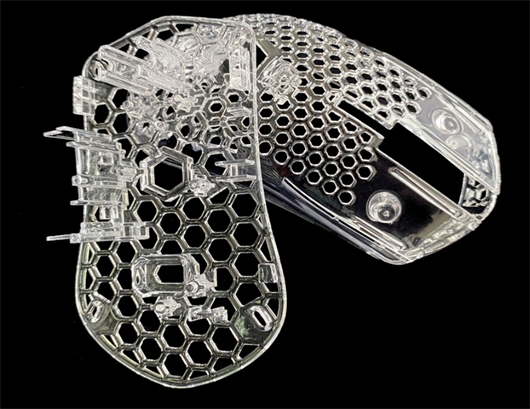
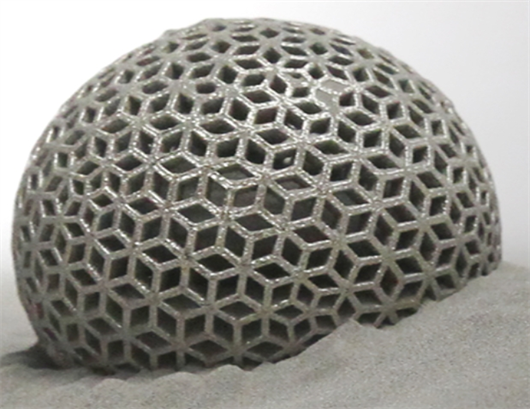
Fast 3D Printing Service
Experience flawless realization of your designs with our professional rapid prototyping 3D printing service. no matter what stage your project is at. Upload your designs for an instant quote and parts as fast as next-day.
What Is 3D Printing?
3D Printing refers to additive manufacturing techniques that build parts by layering materials. Rapid prototyping 3D printing provides a quick, easy, and cost-effective approach to transform ideas into successful products. These prototypes not only validate designs but also identify potential issues early in the development process, enabling immediate design fixes and avoiding expensive changes during full-scale production.
Parts delivered as fast as 24 hour
43+ material and finishing options
One stop from prototype to production
95% of parts delivered on-time and in-full
Our 3D Printing Processes

Stereolithography (SLA)
A high resolution,production grade technology.

Selective Laser Melting(SLM)
Get quality Metal printing parts at consistently low prices.

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Ideal for functional testing, low to mid volumes.

Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
Accelerate time to market with production-grade 3D printing.

Digital Light Process(DLP)
Ideal for create parts that are very rich in detail.

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Low cost process for early stage prototypes.

Carbon Digital Light Synthesis (DLS)
Production speed and repeatability for end-use parts.
What Are The Pros of 3D Printing?
- Accelerated Development: The integration of 3D printing expedites product development and empowers engineers to swiftly iterate on prototypes.
- Affordability: Cost-effective alternatives in the form of less advanced machines are readily available. Nonetheless, the parts manufactured by these machines have restricted industrial capabilities.
- User-Friendly: 3D printers have become increasingly user-friendly, eliminating the need for extensive expertise to operate them. Slicing software efficiently translates the parts into printable layers, while the machines are pre-configured for optimal performance.
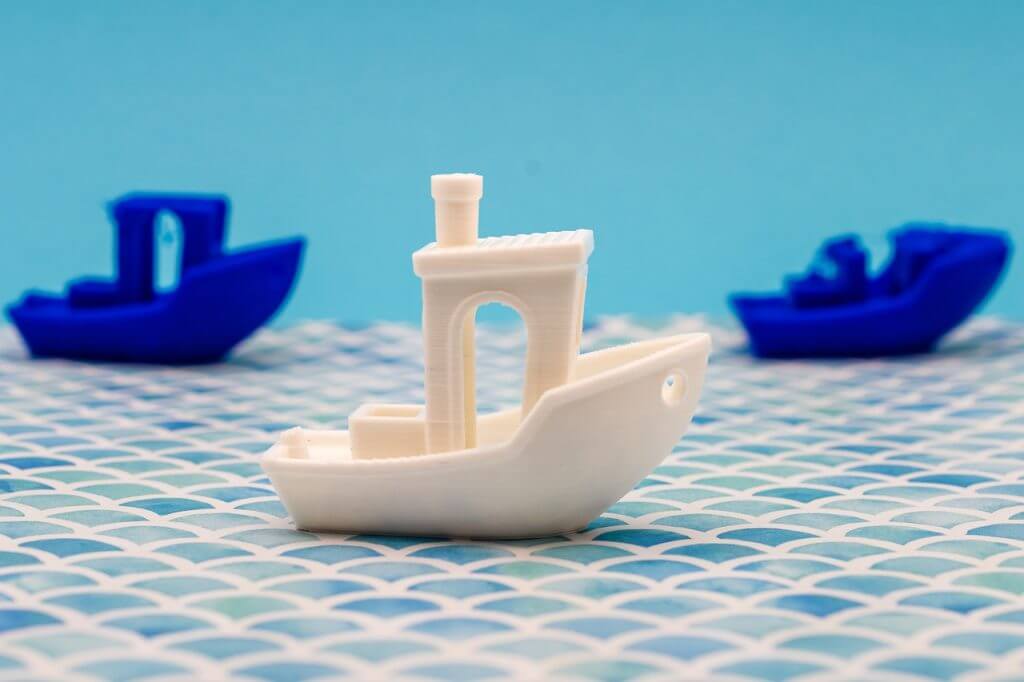
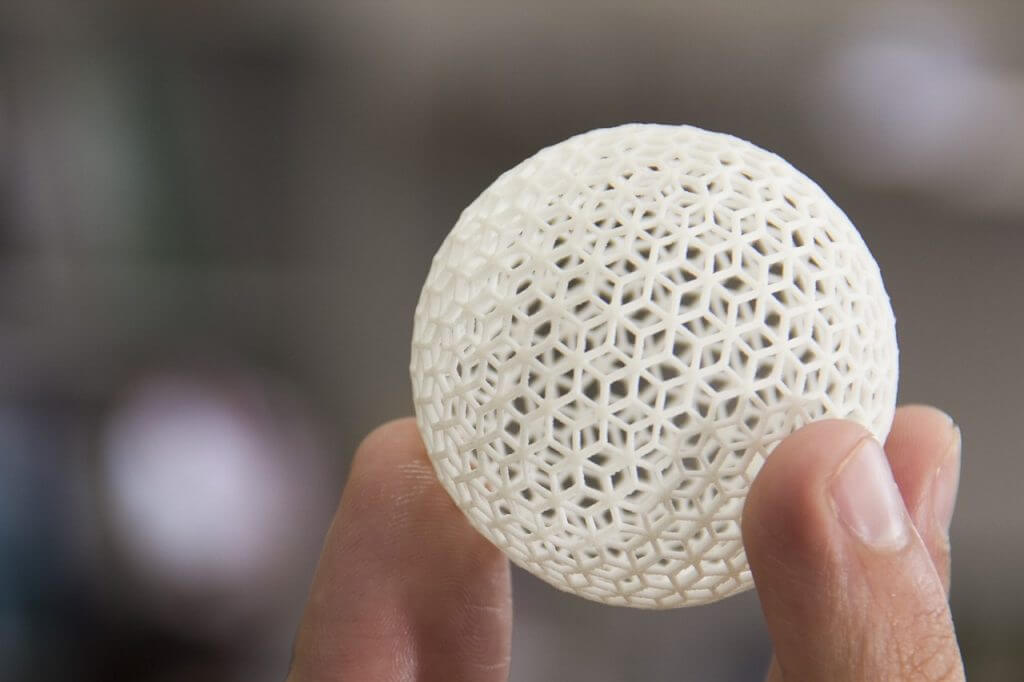


Applications of 3D Printing
Applications of SLA 3D Printing
Creating concept models
Designing presentation prototypes
Producing clear prototypes
Developing master patterns for silicone molding
Applications of SLS 3D Printing
Developing functional prototypes
Fabricating engineering test parts
Producing end-use production parts
Incorporating complex ducts, snap fits, and living hinges
From Prototyping to Production
Seamlessly progressing your design from inception to full-scale production is now effortless with Kevorapid. Our streamlined sourcing solution simplifies the acquisition of prototypes, models, and production parts, making us your go-to partner for success.
3D printing
Prompt parts for early-stage design assessment: fit, form, or function testing.
Urethane Casting
Enhanced prototypes showcasing both aesthetics and functionality for mid-stage development evaluations.
Injection Molding
100% production quality parts for testing, bridge production, and full production stages.
3D Printing Vs CNC Machining: Choose Right For Your Projects

- Subtractive & Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer, offering several advantages over traditional manufacturing. However, it does come with its own set of challenges. On the other hand, CNC machining is a commonly used subtractive technique that involves cutting off material from the blank to create parts.
- Materials & Availability
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds parts layer by layer, offering several advantages over traditional manufacturing. However, it does come with its own set of challenges. On the other hand, CNC machining is a commonly used subtractive technique that involves cutting off material from the blank to create parts.
- Subtractive & Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, builds parts through layered materials, providing multiple advantages over traditional manufacturing. However, it does encounter certain issues. On the other hand, CNC machining is a commonly employed subtractive technique for parts production, where parts are created by cutting off material from a blank.
- Materials & Availability
In 3D printing, parts are formed layer by layer using materials such as liquid photopolymer resins, photopolymer drops, plastic or metal powders, and plastic filaments. This process generates less waste than CNC machining, where parts are cut from a whole piece of material, leading to relatively low material utilization. However, CNC machining has the advantage of compatibility with a wide range of materials, including production-grade engineering plastics and various metals. This makes CNC machining the preferred technique for prototypes and mass-produced parts requiring high functionality and special performance.

3D Printed Parts Made by Kevorapid