
PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PLA+ are two materials that have attracted a lot of attention in 3D printing and many other applications.
Despite their similar names, they each exhibit unique properties and application advantages.
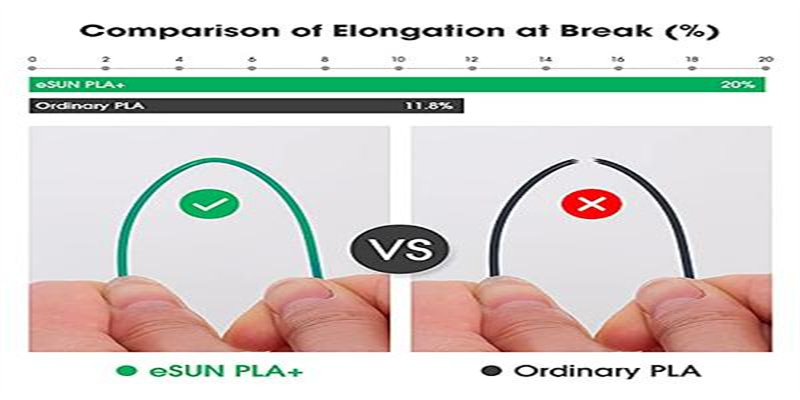
PLA, an environmentally friendly material derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, has won wide recognition for its
excellent printing performance. Its printing process is smooth, and the finished product has a smooth and delicate surface, which
can be beautifully printed without the need to close the cavity. The low shrinkage rate and the fact that it is not easy to warp or crack
make PLA the material of choice for large-size model printing. In addition, PLA wire has no irritating odor release during the printing
process and is FDA approved, ensuring safety and reliability of use. However, standard PLA has a relatively low melting point and is
prone to absorbing moisture from the air, which limits its use in high-temperature environments and makes it brittle when subjected
to large external forces
 .
.
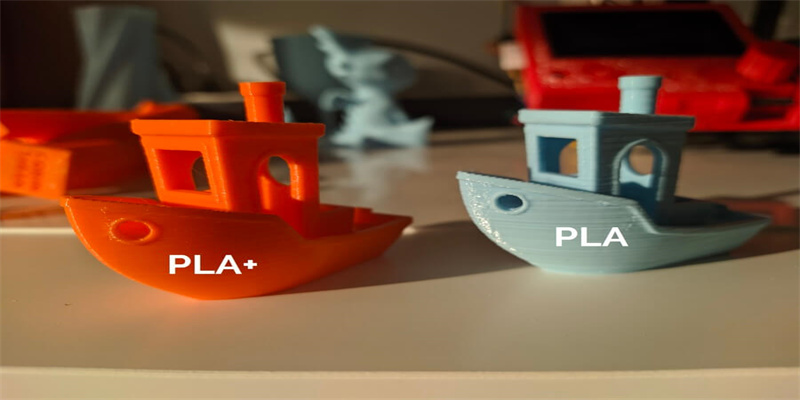
In contrast, PLA+, as an upgraded version of PLA, not only retains its easy-to-print characteristics, but also realizes significant
improvements in toughness and interlayer bonding. Compared to traditional PLA wire, PLA+ exhibits higher toughness, rigidity
and impact resistance, with tougher lines that are less likely to break. These performance improvements allow PLA+ to excel when
printing functional parts, especially for applications that require high impact resistance. For example, when manufacturing
automotive interior parts, PLA+ can effectively absorb collision energy and protect passengers due to its excellent toughness
and impact resistance.

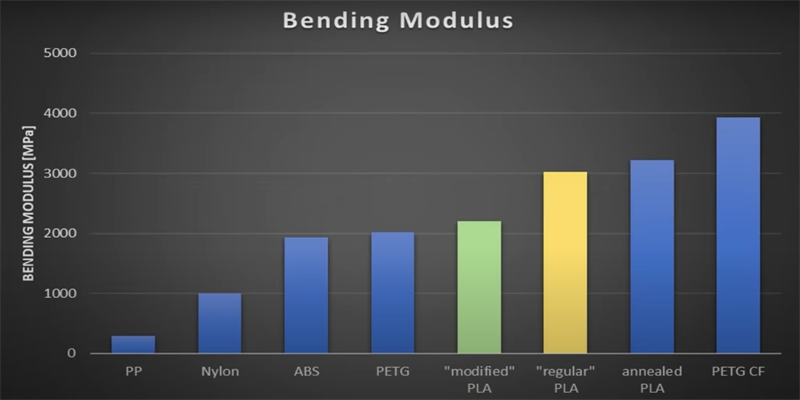
In the field of 3D printing, the emergence of PLA+ undoubtedly provides more possibilities for material selection. It not only
solves the limitations of standard PLA under high temperature and strong force, but also broadens the scope of application of
the material. While both are environmentally friendly materials and both support post-treatment processes such as sanding,
painting and bonding, PLA+ offers a comprehensive upgrade in performance that makes it more suitable for parts that need
to withstand higher stresses. For example, in the aerospace sector, PLA+ is widely used in the manufacture of aircraft interiors
and components due to its excellent rigidity and toughness, effectively enhancing the safety and durability of aircraft.
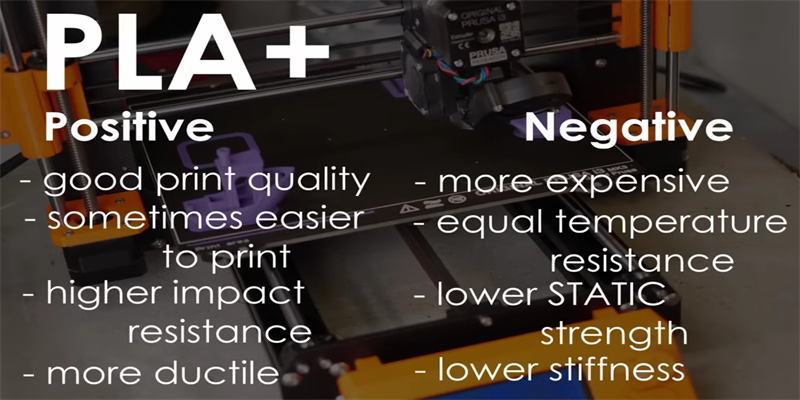
To summarize, despite the similarities between PLA and PLA+ in many aspects, PLA+’s significant improvement in
toughness and impact resistance allows it to show unparalleled advantages in specific application scenarios. Therefore,
when choosing a material, we should take into account the specific needs and application scenarios in order to make the
most informed decision. Whether in automotive manufacturing or aerospace, PLA+ has won wide acclaim and applications
for its outstanding performance.